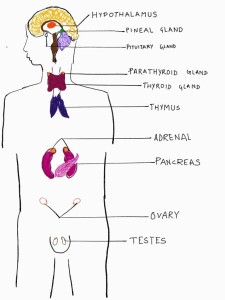
ANIMAL HORMONES
Hormones are chemical substances secreted from ductless endocrine glands into blood. They act on target organs and carry on specific functions. Different hormones have different target organs and functions. Hormones are amino acid, protein, steroid and peptides derivatives.
Video link summarizing this chapter:
Different types of Hormones their origin and function
| Anterior Lobe of Pituitary Gland |
*ACTH ( Adreno Cortico Trophic Hormone) – It Stimulates synthesis of corticosteroid hormones (glucocorticoid and androgen ) from adrenocortical cells of adrenal glands. * FSH ( Follicle stimulating hormone) – In female stimulates maturation of graafian follicle in ovary and in male helps in spermatogenesis by production of androgen binding protein. *Growth Hormone ( GH) – Stimulates protein synthesis, growth and reproduction * Lipotropin ( LPH)- Lypolysis; Stimulates melanocytes to produce melanin *Luteinizing Hormone ( LH) – In female stimulates ovary to produce estrogen and progesterone and helps in ovulation; in male it stimulates to produce testosterone *Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone ( MSH) – Melanogenesis by melanocytes in skin and hair. *Prolactin – Milk production in mammary gland *Thyroid Stimulating hormone (TSH) – Stimulates thyroid gland to produce Thyroxine hormone ( T3) and T4. |
|
| Posterior Pituitary |
*Antidiuretic hormone ( ADH)/ Vasopressin – Helps in retention of water in kidney.Stimulates release of ACTH in anterior pituitary *Oxytocin – Stimulates breast milk production.Contraction and relaxation of cervical muscles.
|
|
| Hypothalamus |
*Corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)- Helps to release ACTH from anterior pituitary * Gonadotropin releasing Hormone ( GnRH) – Helps to release of FSH and LH from anterior pituitary gland. *Orexin– Wakefulness and increased energy expenditure, increased appetide. *Prolactin releasing hormone ( PRH)- Release prolactin from anterior pituitary gland * Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH) – Helps to release thyroid stimulating hormone from anterior pituitary
|
|
| Pineal gland | *Melatonin- Regulates biological circadian rhythm | |
| Thyroid gland |
*Thyroxine T3 and T4 – It helps to increase cell metabolism, essential for growth and neural development. *Calcitonin- It helps in bone construction and reduction of Ca++ from blood. |
|
| Parathyroid gland | *Parathyroid hormone – It increases osteoclast ie, release of Ca++ from bone and reabsorption of it by kidney. It also decreases uptake of Phosphate in kidney but increases its uptake from bone. In both the process it triggers Vit D activity. | |
| Adrenal gland |
*Epinephrine or Adrenalin( secreted from adrenal medulla) – Helps to maintain blood pressure level, fight or fight response, so it is also known as emergency hormone. *Androgen ( Adrenal cortex)- It acts as a substrate for estrogen * Cortisol or glucocortocoid (Adrenal Cortex) – Stimulate gluconeogenesis; stimulation of breakdown of fat; anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive *Mineralocorticoid or Aldosterone ( adrenal cortex) – Increases blood volume by reabsorption of Na; K+ and H+ in kidney |
|
| Pancreas |
*Amylin – Slows down gastric emptying, secretion of digestive juices, and reduces intake of food. *Glucagon –It helps in conversion of glycogen stored in liver to glucose( Glycogenolysis), which is then released into blood stream. It also helps in gluconeogenesis. *Insulin – Released from islets of langerhans. Helps to maintain balanced glucose level in blood by conversion of glucose to glycogen in liver( glycogenesis, glycolysis) and muscle; intake of lipids from blood and synthesis of triglycerides in adipocytes. ( malfunction of insulin production give rise to Type I diabetes/ Juvenile diabetes ( when the body does not produce insulin) , Type II diabetes ( when body fails to produce required amount of insulin) *Pancreatic polypeptide – Maintains gastrointestinal secretion. *Somatostatin – Slows down release of insulin and glucagon. |
|
| Liver |
*Angiotensinogen and angiotensin – Vasoconstriction; induces release of aldostrerone from adrenal cortex *Hepcidin – Inhibits iron export from cell * Insulin like growth factor or Somatomedin – Regulates cell growth and development
|
|
| stomach |
*Ghrelin – Stimulate apetite, and secretion of growth hormone from anterior pituitary *Gastrin – Secretion of gastric juices |
|
| Duodenum |
*cholecystokinin – Release of digestive enzyme and bile from pancreas and liver respectively. *Secretin – Secretion of bicarbonates from liver, pancreas and duodenal Brunner’s gland. Ehances effects of Cholecystokinin. |
|
| Small Intestine | *Motilin – Stimulates gastric activity. | |
| Heart |
*Atrial – natriuretic peptide – Acts as a powerful vasodialator, maintains homeostatic control of body. *Brain – natriuretic peptide– Reduces vascular resistance, reduces blood, water sodium and fat
|
|
| Ovary |
*Oestrogen– Acts as the main sex organ and helps in development of primary and secondary sex characters in females *Progesteron – Supports pregnancy. It helps in thickening of the wall of the endometrial lining; It helps in carrying out proper menstrual cycle, pregnancy and embryogenesis. |
|
| Testes |
*Testosterone – Development and growth of male sex organs and secondary sex characters of male like beard, hair, deepening of voice etc. *Antimullerian hormone(AMH) – Secreted by sertolli cells of testes.It Inhibit release of prolactin and TRH from anterior pituitary gland in male.Other major function is to inhibit the development of mullerian duct in males. *Inhibin – Inhibit production of FSH |
|
| Thymus | Thymosine- It helps in maturation of T- lymphocytes. | |
.
*Peptide derivative * Amino acid derivative * Steroid
|
BEES FACTS
Diabetes Type 1(Juvenile diabetes, the pancreas fails to produce insulin), Diabetes Type 2( normally occurs after 40 years of age and is associated with reduced production of insulin or body becomes resistant to insulin) , and gestational diabetes( happens during pregnancy).
|